

These synergies can interfere with walking and standing. The anterior tibial artery supplies the anterior extensor compartment and. The extensor synergy of the arm involves many of the opposite movements, including: shoulder adduction (reaching inward) elbow extension pronation (palm facing downward) wrist extension and finger flexion (these postures may vary) Flexor and extensor synergies are also seen in the legs. Actions: Flexion of the lateral four toes. Attachments: Originates from the medial surface of the tibia and attaches to the plantar surfaces of the lateral four digits.
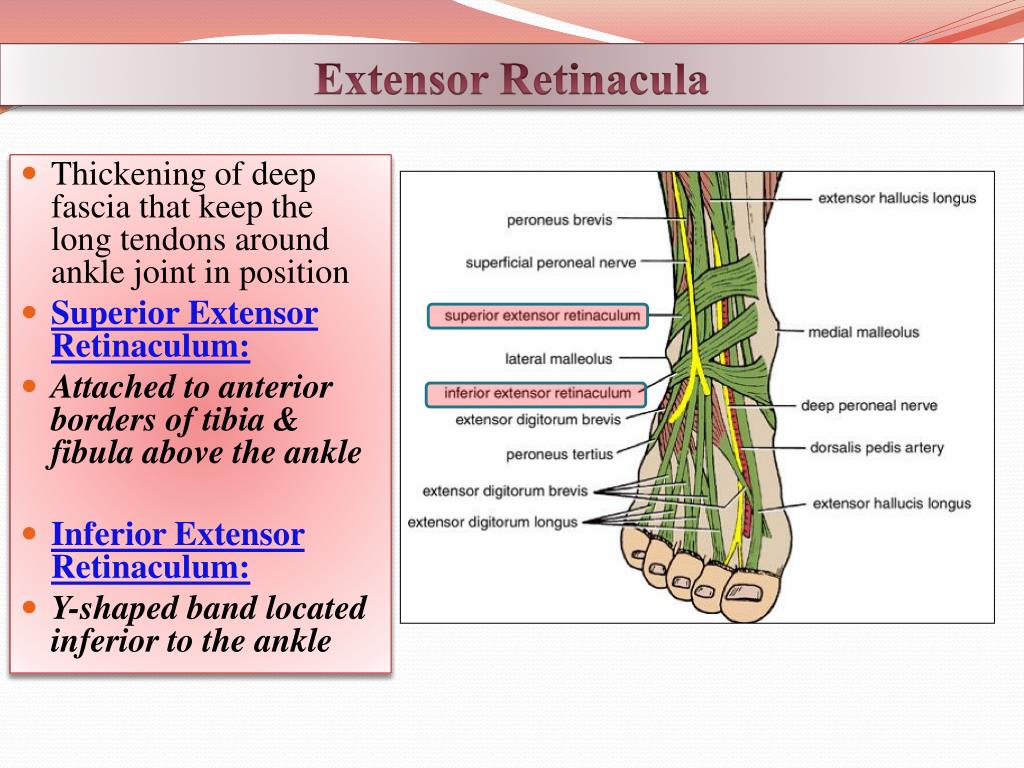
The fibres converge into a tendon, which travels onto the dorsal surface of the foot. Attachments: Originates from the lateral condyle of the tibia and the medial surface of the fibula. Its four tendons can be palpated on the dorsal surface of the foot. splits into deep fibular nerve and superficial fibular nerve The deep fibular nerve pierces through the _ to enter the anterior compartment of the leg. The lower limb is supplied by the femoral artery, which is a continuation of. All of these activities overload the anterior compartment muscles, producing pain in the antero-lateral area of the leg along the extensor tendons of the. The flexor digitorum longus is a thin muscle and is located medially within the posterior leg. The extensor digitorum longus lies laterally and deep to the tibialis anterior. What artery supplies the arteries of the anterior compartment? anterior tibial artery What is the pathway of the anterior tibial artery? descends on the anterior surface of the interosseeous membrane with the deep fibular nerve (in groove between tibialis anterior and extensor hallucis longus)Ĭrosses the ankle midway between the lateral and medial malleolusĬontinues onto the foot as the dorsalis pedis artery What muscles in the thigh does the common fibular nerve run on? on tendon of biceps femoris What compartment does the common fibular nerve enter and what does it split into? lateral compartment


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
